PICARD mission and the design of BOS sensor
SUN, a variable star, its activities are directly impacting on the climate of the Earth. In order to study the Sun-Earth climate connections, the PICARD satellite was launched at June, 2010. The payload instruments are focusing on:
- The solar diameter measurements.
- Heloseismology.
- Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) monitoring.
- Spectral Irradiance of the Sun.
- Solar activities and the Earth’s climate.
The BOS (Bolometric Oscillation Sensor ) is a part of the SOVAP (SOlar VAriability for PICARD ) experiment. SOVAP is composed with the absolute radiometer DIARAD (DIfferential Absolute RADiometer), which is carrying out the total solar irradiance monitoring, and the BOS, which is operated continually with a 10 seconds cadence to fill the time gaps between opening and closure phases of the DIARAD absolute radiometer.
Electromagnetic radiation measurement basic in space
Suppose solar photons are projected on a grey disk plate (figure blow),
it receives solar radiation at the front plate:
(1) ![]()
Where ![]() , incoming energy,
, incoming energy, ![]() absorption of the disk plate,
absorption of the disk plate, ![]() , solar irradiance,
, solar irradiance, ![]() , radius of the disk. According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law, the energy will be remitted back to the Space by the front and back surface area of the disk if the thickness of the disk is negligible.
, radius of the disk. According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law, the energy will be remitted back to the Space by the front and back surface area of the disk if the thickness of the disk is negligible.
(2) ![]()
![]() , emissivity of disk plate,
, emissivity of disk plate, ![]() Stefan-Boltzmann constant. Let
Stefan-Boltzmann constant. Let ![]() , we can find solar irradiance
, we can find solar irradiance ![]() by measuring brightness temperature
by measuring brightness temperature ![]() .
.
(3) ![]()
In practice, it is more complicated. Firstly, it is impossible to know the surface temperature of the disk without using measurement elements, thermistors, power supply, resistances, amplifier etc. Once the electronics are setting nearby the detector, or to say, the detector is a part of an instrument, then the ![]() . The temperature measured is also related to the environments. In addition,
. The temperature measured is also related to the environments. In addition, ![]() and
and ![]() is degrading with time. Thus, in order to conduct the correct experiment for the temperature measurement, the
is degrading with time. Thus, in order to conduct the correct experiment for the temperature measurement, the ![]() must be measured as near as possible the value of
must be measured as near as possible the value of ![]() . Secondly, for instance, if the sensing unit is orbiting Earth, the measured temperature is not only solar origin, but also related to the reflected visible and remitted infrared radiation from the top of the atmosphere and plus the ambient noise from the satellite environment.
. Secondly, for instance, if the sensing unit is orbiting Earth, the measured temperature is not only solar origin, but also related to the reflected visible and remitted infrared radiation from the top of the atmosphere and plus the ambient noise from the satellite environment.
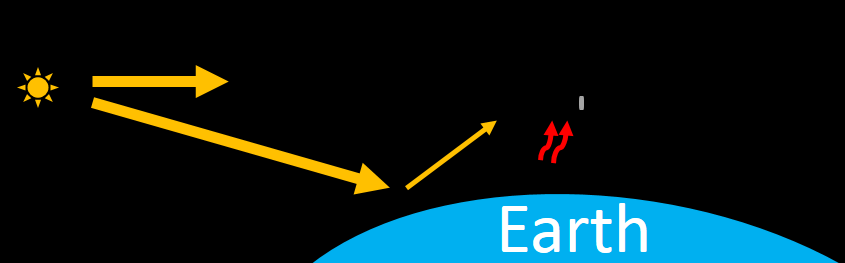 The challenge is obvious. How to measure the electromagnetic radiation from Sun and Earth at the same time as the sketch showed above, meanwhile to minimize the ambient thermal noise? Which is also the goals of PICARD-BOS.
The challenge is obvious. How to measure the electromagnetic radiation from Sun and Earth at the same time as the sketch showed above, meanwhile to minimize the ambient thermal noise? Which is also the goals of PICARD-BOS.
Scientific Objectives of PICARD-BOS
- Monitoring the incoming total solar irradiance with high cadence
 solar normal modes.
solar normal modes. - Tracking the outgoing terrestrial radiation at the top of the atmosphere
 Earth’s radiation budget experiment.
Earth’s radiation budget experiment.
Design philosophy to meet the challenges
- ‘Continuously’ measurements with a ten seconds sampling period
 get the normal modes.
get the normal modes. - The sensor has a hemispherical field of view (HFOV), which is looking at the Sun as well as the Earth at the same time
 terrestrial outgoing radiation at the top-of-atmosphere.
terrestrial outgoing radiation at the top-of-atmosphere. - The main detector is thermal isolated from the environment.
The schema shows the configuration and the working principle of BOS. The main detector is thermally isolated from the satellite. The temperature of the black surface is recorded by the fist NTC thermistor ![]() , which is directly related to the electromagnetic radiation of Sun and Earth. The second NTC thermistor
, which is directly related to the electromagnetic radiation of Sun and Earth. The second NTC thermistor ![]() is measuring the temperature of a junction where the lighter mass
is measuring the temperature of a junction where the lighter mass ![]() is connected with a heavier mass
is connected with a heavier mass ![]() . The surface of
. The surface of ![]() was coated in white, which has a lower absorption coefficient compare to the black painting of
was coated in white, which has a lower absorption coefficient compare to the black painting of ![]() . In terms of wavelength, it is only sensitive to the infrared radiation from Earth.
. In terms of wavelength, it is only sensitive to the infrared radiation from Earth. ![]() is cooled by the
is cooled by the ![]() and thermal balance of BOS is reached. It means the thermal gradient between
and thermal balance of BOS is reached. It means the thermal gradient between ![]() and
and ![]() gives the incoming flux originated from external body.
gives the incoming flux originated from external body.
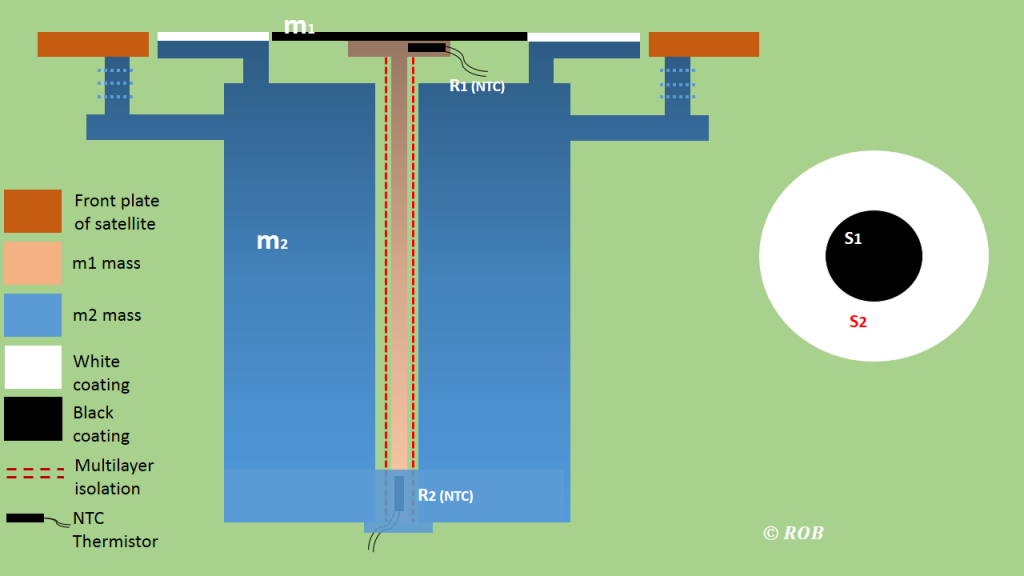
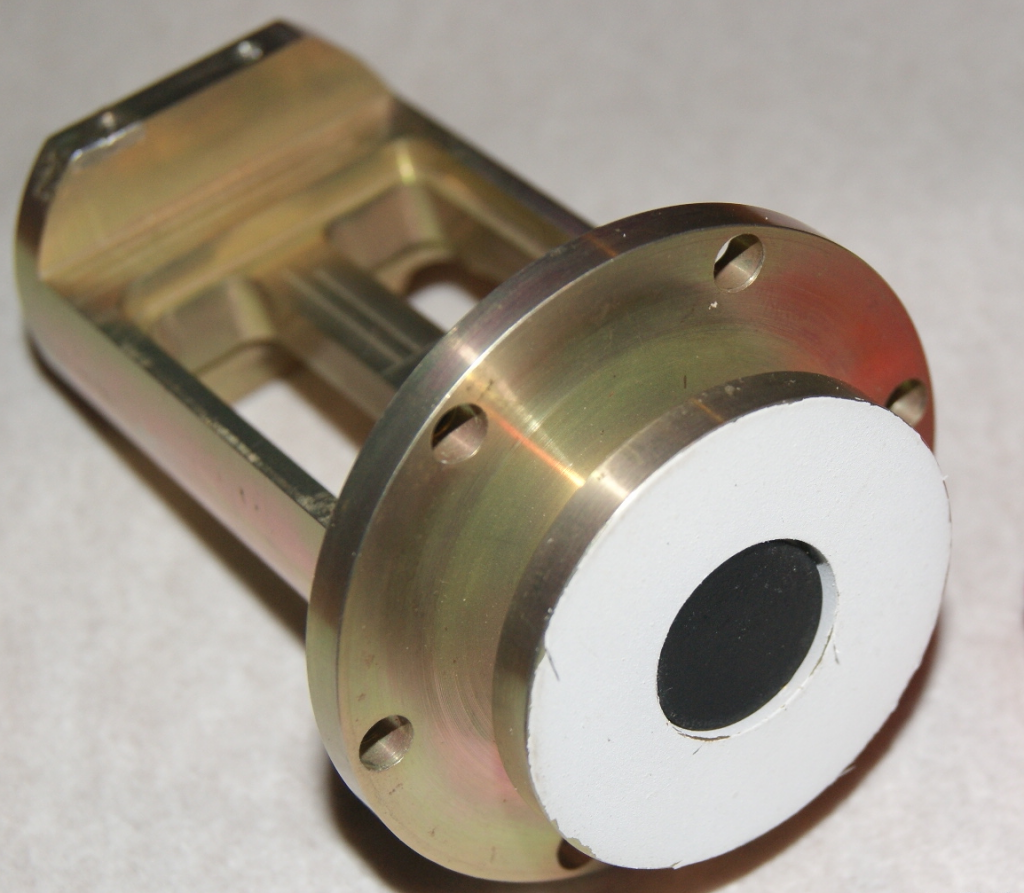
The BOS is composed with two detectors, the black coated detector weighted 8 gram and the white painted detector with a 160 gram heavier mass. The black detector will take all electromagnetic radiation, but the white channel is only sensitive to the infrared radiation. The ![]() detector is completely isolated from the
detector is completely isolated from the ![]() by the multilayer isolation. The sensor unit is passive thermal stabilized by such a configuration. Two NTC thermistors are separately setting up under the surface m1 and at the end of a mechanical shunt, where it is connected to the mass
by the multilayer isolation. The sensor unit is passive thermal stabilized by such a configuration. Two NTC thermistors are separately setting up under the surface m1 and at the end of a mechanical shunt, where it is connected to the mass ![]() . The
. The ![]() mass is fixed to the front plate of the satellite.
mass is fixed to the front plate of the satellite.
The BOS mechanical part of flying and ground spare model were made at the workshop of Royal Observatory of Belgium. The surface treatment and the painting finishing was realized by the space qualified engineer of Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium.
Left is the photo of identical ground spared BOS sensor. Right photo was taken after the BOS is integrated with the DIARAD absolute radiometer and the instrument package was under the vibration test.


